#Importance of sustainable urban planning
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Building Sustainable Cities and Communities: The Path to a Greener Future

In today's rapidly urbanizing world, the concept of sustainability has become more important than ever. Goal 11 of the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) focuses on creating sustainable cities and communities. With the global population projected to reach 9.8 billion by 2050, the need for sustainable urban planning and development is paramount. This article explores the significance of Goal 11 and highlights the key strategies and initiatives required to build greener, more resilient cities and communities.
Understanding Goal 11
Goal 11 of the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) has a comprehensive vision for cities and human settlements. It recognizes the importance of inclusivity, safety, resilience, and sustainability in urban areas. By addressing various aspects of urban development, Goal 11 aims to create thriving communities that prioritize the well-being of their residents and the environment.
One of the key objectives of Goal 11 is to ensure the availability of affordable housing. Access to adequate, safe, and affordable housing is a fundamental right for all individuals. However, in many urban areas, housing affordability has become a significant challenge, leading to homelessness and housing insecurity. Goal 11 emphasizes the need to implement policies and initiatives that promote affordable housing options. This can be achieved through social housing programs, rent control measures, and housing subsidies. By ensuring affordable housing, cities can address social inequality, provide stability to residents, and foster inclusive communities.
Sustainable transport systems are another crucial aspect of Goal 11. Transportation is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution in cities. To create sustainable cities and communities, it is essential to prioritize low-carbon and efficient transportation options. This includes expanding public transportation networks, encouraging cycling and walking infrastructure, and promoting the use of electric vehicles. By shifting away from private vehicles and promoting sustainable modes of transportation, cities can reduce congestion, improve air quality, and enhance mobility for all residents.
Efficient waste management is also highlighted in Goal 11. As cities grow, waste generation increases, posing significant environmental challenges. Sustainable waste management practices are crucial to minimize the environmental impact of urban areas. Goal 11 encourages the adoption of integrated waste management systems that prioritize waste reduction, recycling, and resource recovery. This can be achieved through initiatives such as waste segregation, composting, and the establishment of recycling facilities. Effective waste management not only helps reduce environmental pollution but also promotes the concept of a circular economy, where resources are used efficiently and waste is minimized.
Access to green spaces is another essential element of sustainable cities and communities. Urban areas often face challenges related to limited green areas and a lack of connection with nature. Goal 11 recognizes the importance of green infrastructure, which includes parks, urban forests, green roofs, and other natural elements integrated into the built environment. These green spaces provide numerous benefits, including improved air quality, reduced heat island effect, enhanced biodiversity, and increased recreational opportunities. By incorporating green spaces into cities, residents can have access to nature, promoting physical and mental well-being.
Preserving cultural heritage is a crucial aspect of Goal 11. Cities and communities are rich in history, culture, and traditions that contribute to their identity and uniqueness. Goal 11 emphasizes the need to safeguard cultural heritage sites, historic buildings, and traditional practices. By preserving cultural heritage, cities can maintain a sense of identity, promote cultural diversity, and attract tourism and economic opportunities. This preservation contributes to the social fabric and vibrancy of cities, making them more sustainable and livable.
By implementing the objectives of Goal 11, societies can enhance the quality of life for residents, reduce environmental impacts, and promote economic growth. Sustainable cities and communities prioritize the well-being of their residents, ensure social equity, and protect the environment. They provide affordable housing options, efficient transport systems, proper waste management, access to green spaces, and preserve cultural heritage. Ultimately, the successful implementation of Goal 11 leads to inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable urban areas that benefit present and future generations.
Sustainable Urban Planning
Sustainable urban planning is a key factor in the successful achievement of Goal 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities. It focuses on designing cities and communities that are not only visually appealing and functional but also prioritize environmental sustainability, resource efficiency, and the well-being of residents.
One of the primary principles of sustainable urban planning is the concept of compact cities. This approach encourages the development of cities that are designed to be dense and compact, rather than sprawling outward. Compact cities promote the efficient use of land, resources, and infrastructure. By concentrating development within a smaller footprint, compact cities minimize urban sprawl, preserve valuable agricultural land and natural habitats, and protect ecosystems. This approach also helps to reduce the need for long commutes, as essential services, amenities, and employment opportunities are located within close proximity to residential areas.
Well-connected cities are another crucial aspect of sustainable urban planning. The goal is to create cities and communities where different neighborhoods and areas are easily accessible to one another. This can be achieved through the design and implementation of a comprehensive transportation network that prioritizes public transportation over private vehicles. Robust public transportation systems, including buses, trains, and light rail, can reduce traffic congestion, lower carbon emissions, and enhance mobility for residents. Additionally, sustainable urban planning promotes the development of pedestrian-friendly infrastructure and encourages the use of bicycles, further reducing reliance on private vehicles and promoting active and healthy lifestyles.
Renewable energy plays a significant role in sustainable urban planning. The transition to clean and renewable energy sources is essential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. Sustainable cities and communities incorporate renewable energy technologies, such as solar panels and wind turbines, into their infrastructure. By integrating renewable energy sources, cities can reduce their dependence on fossil fuels for electricity generation, mitigate air pollution, and contribute to a greener and more sustainable energy future.
Sustainable urban planning also emphasizes mixed land-use development. This approach seeks to create neighborhoods and areas where residential, commercial, and recreational spaces coexist in close proximity. Mixed land-use development reduces the need for long-distance travel and promotes walkability. It allows residents to access essential services, educational institutions, employment opportunities, and recreational facilities without having to rely heavily on private vehicles. By integrating various land uses, sustainable urban planning fosters vibrant and diverse communities that promote social interaction and economic vitality.
Furthermore, sustainable urban planning takes into account the importance of green infrastructure. This involves incorporating green spaces, parks, and natural elements into the urban fabric. Green infrastructure provides numerous benefits, such as improved air quality, temperature regulation, stormwater management, and biodiversity conservation. Parks and green spaces offer recreational opportunities, enhance the aesthetic appeal of cities, and contribute to the overall well-being and quality of life of residents.
In conclusion, sustainable urban planning is crucial for achieving Goal 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities. By designing cities and communities that are compact, well-connected, and resource-efficient, we can minimize urban sprawl, protect ecosystems, and reduce carbon emissions. Sustainable urban planning promotes mixed land-use development, prioritizes public transportation, and encourages the use of renewable energy sources. It also recognizes the importance of green infrastructure and the integration of natural elements into urban environments. By embracing sustainable urban planning principles, cities and communities can create a more sustainable, livable, and resilient future for all.
Green Infrastructure
Green infrastructure plays a vital role in creating sustainable cities and communities. It refers to the integration of natural elements, such as parks, green roofs, urban forests, green walls, and permeable surfaces, into the built environment. By incorporating these green spaces into cities and communities, numerous benefits are realized, positively impacting both the environment and the well-being of residents.
One significant advantage of green infrastructure is the improvement of air quality. Trees, plants, and vegetation help absorb pollutants such as carbon dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, and particulate matter from the air. Through the process of photosynthesis, plants release oxygen and filter harmful substances, leading to cleaner and healthier air. This reduction in air pollution contributes to the overall improvement of public health, as exposure to pollutants is linked to respiratory diseases and other health issues.
Another benefit of green infrastructure is the mitigation of the urban heat island effect. Urban areas tend to have higher temperatures than surrounding rural areas due to the concentration of buildings, roads, and concrete surfaces that absorb and retain heat. By incorporating green spaces, such as parks and urban forests, cities can create pockets of vegetation that provide shade and evaporative cooling, reducing ambient temperatures. This helps create a more comfortable and livable environment, particularly during hot summer months.
Green infrastructure also enhances biodiversity within urban areas. Traditional urban development often results in the destruction of natural habitats and fragmentation of ecosystems. By incorporating green spaces, cities can create corridors and habitats that support a variety of plant and animal species. These spaces provide shelter, food sources, and nesting areas, promoting biodiversity and ecological balance within the urban environment. By fostering biodiversity, cities can create resilient ecosystems that can adapt to environmental changes and provide ecosystem services.
In addition to the environmental benefits, green infrastructure also provides social and economic advantages. Access to green spaces has been shown to have a positive impact on mental health and well-being. People living in areas with green infrastructure have increased opportunities for outdoor activities, exercise, and relaxation, which can reduce stress, improve mood, and enhance overall quality of life. Green spaces also provide opportunities for social interaction and community engagement, fostering a sense of belonging and community cohesion.
Furthermore, incorporating green infrastructure into cities and communities contributes to economic prosperity. Green spaces attract tourism and visitors, generating revenue for local businesses. Properties located near green spaces often experience increased value, leading to economic benefits for property owners. Green infrastructure also has the potential to create job opportunities, particularly in the areas of park maintenance, landscaping, and urban forestry.
To fully realize the benefits of green infrastructure, strategic planning and implementation are essential. Cities and communities need to consider factors such as appropriate land allocation, connectivity of green spaces, and community engagement in the planning process. Collaboration between urban planners, architects, landscape designers, environmental experts, and community stakeholders is crucial to ensure the successful integration of green infrastructure into the urban fabric.
Green infrastructure plays a significant role in creating sustainable cities and communities. By integrating natural elements into the built environment, cities can reap a multitude of benefits. Improved air quality, reduced urban heat island effect, enhanced biodiversity, and increased recreational opportunities are among the advantages of green infrastructure. Moreover, it fosters a healthier and more livable environment, positively impacting the physical and mental well-being of residents. By prioritizing and investing in green infrastructure, cities can create sustainable, resilient, and vibrant urban spaces for present and future generations.
Affordable Housing
The lack of affordable housing is a significant challenge faced by many urban areas around the world. It is a complex issue that affects individuals and communities, impacting their overall well-being and quality of life. Goal 11 of the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals recognizes the importance of addressing this challenge and emphasizes the need to ensure access to adequate, safe, and affordable housing for all.
Affordable housing refers to housing options that are within the financial means of individuals and families, considering their income levels. It is a fundamental right that enables individuals to live in safe and decent conditions, fostering stability and security. However, in many cities, the cost of housing has escalated significantly, making it unaffordable for a significant portion of the population, particularly low-income households.
To address this issue, Goal 11 encourages the implementation of policies and initiatives that promote affordable housing options. One approach is through the establishment of social housing programs. Social housing involves the provision of housing units at below-market rates to individuals and families who are unable to afford market-rate housing. These programs are often administered by government agencies or non-profit organizations and aim to provide affordable and stable housing for those in need. Social housing plays a crucial role in addressing homelessness, reducing housing inequality, and promoting social stability.
Rent control measures are another policy tool used to promote affordable housing. Rent control laws set limits on the amount landlords can increase rents, providing stability for tenants and preventing excessive rent hikes. These measures aim to protect vulnerable populations from the risk of displacement due to rising housing costs. Rent control can help maintain affordable housing options in areas where market forces would otherwise drive up rents, allowing individuals and families to remain in their homes and communities.
In addition to social housing and rent control, the provision of housing subsidies is another strategy to promote affordable housing. Housing subsidies are financial assistance programs that help low-income individuals and families cover the cost of housing. These subsidies can come in the form of rental assistance, such as Section 8 vouchers in the United States, or direct financial assistance to support homeownership. Housing subsidies help bridge the gap between income levels and housing costs, making housing more affordable and accessible to those in need.
Promoting affordable housing not only addresses the immediate issue of homelessness and housing insecurity but also contributes to social stability and inclusive communities. Access to affordable housing allows individuals and families to establish roots, build community connections, and contribute to the local economy. It fosters a sense of stability and security, providing a foundation for individuals to pursue education, employment, and other opportunities that contribute to their overall well-being. Affordable housing also helps prevent the displacement of vulnerable populations, preserving the social fabric and diversity of communities.
However, addressing the lack of affordable housing requires a multi-faceted approach and collaboration between various stakeholders. Governments, policymakers, urban planners, and community organizations play a crucial role in implementing effective strategies and initiatives. It is essential to consider factors such as land use planning, zoning regulations, construction costs, and the availability of financing mechanisms to support affordable housing development.
Furthermore, affordable housing initiatives should prioritize sustainable and energy-efficient design and construction practices. This not only reduces the environmental impact of housing but also lowers ongoing utility costs for residents, making housing more affordable in the long run. The integration of affordable housing with transportation hubs, amenities, and employment opportunities is also important to ensure that residents have access to essential services and can minimize transportation costs.
The lack of affordable housing is a critical challenge in urban areas, impacting the well-being and quality of life of individuals and communities. Goal 11 recognizes the importance of ensuring access to adequate, safe, and affordable housing for all. Through the implementation of policies and initiatives such as social housing programs, rent control measures, and housing subsidies, affordable housing options can be promoted. Affordable housing contributes to social stability, inclusive communities, and provides individuals and families with a foundation for economic and personal development. Addressing the issue of affordable housing requires a comprehensive and collaborative approach, involving governments, policymakers, urban planners, and community organizations to create sustainable and inclusive cities and communities
Sustainable Transport Systems
Transportation plays a significant role in urban areas, connecting people to their workplaces, schools, healthcare facilities, and leisure activities. However, traditional transportation systems heavily rely on fossil fuels, resulting in substantial greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. Goal 11 of the Sustainable Development Goals recognizes the need to develop sustainable transport systems that are accessible, affordable, and low-carbon, in order to create more sustainable cities and communities.
One of the key objectives of Goal 11 is to expand public transportation networks. Public transportation, such as buses, trams, and trains, offers an efficient and environmentally-friendly alternative to private vehicles. By investing in the expansion and improvement of public transportation infrastructure, cities can provide residents with reliable and affordable transportation options. This reduces the reliance on private cars, which contribute significantly to congestion, air pollution, and carbon emissions. Accessible and well-connected public transportation systems also promote social inclusivity by ensuring that individuals of all socioeconomic backgrounds have equal access to transportation services.
Promoting cycling and walking is another crucial aspect of sustainable transportation. Encouraging these modes of transportation not only reduces reliance on fossil fuels but also promotes active and healthy lifestyles. Cities can invest in infrastructure that supports safe and convenient cycling and walking, such as dedicated bike lanes, pedestrian-friendly sidewalks, and bike-sharing programs. These initiatives not only contribute to reduced traffic congestion and improved air quality but also enhance the overall well-being of residents by encouraging physical activity and reducing sedentary lifestyles.
Furthermore, Goal 11 promotes the use of electric vehicles (EVs) as a sustainable transportation option. Electric vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, reducing local air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. To support the adoption of EVs, cities can establish charging infrastructure, offer incentives for purchasing EVs, and promote public transportation systems that utilize electric buses and trains. The transition to electric vehicles also contributes to reducing dependence on fossil fuels and promoting the use of renewable energy sources in the transportation sector.
In addition to reducing emissions and air pollution, sustainable transportation systems offer several other benefits. By reducing congestion through the promotion of public transportation and active modes of transportation, cities can improve traffic flow and travel times. This enhances overall mobility and accessibility for all residents, including those who cannot afford private vehicles or have mobility restrictions. Sustainable transportation systems also contribute to improved road safety by reducing the number of vehicles on the road and promoting safer infrastructure for cyclists and pedestrians.
To effectively implement sustainable transportation systems, cities need to adopt integrated and holistic approaches. This involves comprehensive urban planning that considers land use, transportation infrastructure, and public spaces. Planning should prioritize the development of compact, mixed-use neighborhoods that promote walkability and access to public transportation. It is crucial to engage with communities and stakeholders to ensure that transportation systems meet their needs and preferences.
Furthermore, the use of innovative technologies and smart transportation solutions can enhance the efficiency and sustainability of transportation systems. Intelligent transportation systems, such as real-time traffic monitoring, smart traffic signals, and integrated fare payment systems, can optimize transportation operations and improve overall system performance. These technologies can help reduce travel times, enhance user experience, and minimize environmental impacts.
In conclusion, sustainable transportation is a key component of Goal 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities. By promoting the development of accessible, affordable, and low-carbon transportation systems, cities can reduce congestion, improve air quality, and enhance mobility for all residents. Expanding public transportation networks, encouraging cycling and walking, and promoting the use of electric vehicles are important strategies in achieving sustainable transportation goals. To realize the benefits of sustainable transportation, cities should adopt integrated planning approaches, engage with communities, and leverage innovative technologies. By prioritizing sustainable modes of transportation, cities can create healthier, more livable, and environmentally-friendly urban environments.
Waste Management and Recycling
Effective waste management and recycling practices are crucial for creating sustainable cities and communities. The increasing population and urbanization have led to a significant rise in waste generation, posing environmental and health challenges. Goal 11 of the Sustainable Development Goals emphasizes the need for integrated waste management systems that prioritize waste reduction, recycling, and resource recovery.
One of the key objectives of Goal 11 is to promote waste reduction. By implementing waste reduction strategies, cities can minimize the amount of waste generated in the first place. This includes promoting the use of sustainable packaging, encouraging the adoption of reusable products, and raising awareness about the importance of minimizing waste. By reducing the amount of waste generated, cities can conserve natural resources, reduce energy consumption, and minimize the environmental impact associated with waste disposal.
Waste segregation is another essential component of effective waste management. By segregating waste at the source, cities can facilitate the recycling and proper disposal of different types of waste. Proper waste segregation involves separating recyclable materials, such as paper, plastics, glass, and metals, from non-recyclable waste. This allows for the efficient recycling and recovery of valuable resources, reducing the need for raw materials extraction and the associated environmental impact. Waste segregation can be achieved through community education and the provision of recycling bins and collection systems.
Recycling plays a critical role in sustainable waste management. It involves the conversion of waste materials into new products, reducing the demand for virgin materials and conserving natural resources. Cities can establish recycling facilities and collection programs to facilitate the recycling process. Recycling initiatives should be comprehensive and cover a wide range of materials, including paper, plastics, glass, metals, and electronic waste. By promoting recycling and creating an infrastructure to support it, cities can reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills and incineration facilities, thereby minimizing the environmental pollution and greenhouse gas emissions associated with these disposal methods.
Composting is another important practice in sustainable waste management. Organic waste, such as food scraps and yard trimmings, can be composted to create nutrient-rich soil amendments. Composting not only reduces the volume of waste sent to landfills but also produces a valuable resource that can be used in gardening, landscaping, and agricultural activities. Cities can promote home composting, as well as establish community composting programs and composting facilities, to divert organic waste from the waste stream and promote the circular economy.
To ensure the effectiveness of waste management systems, it is crucial to educate and engage communities. Public awareness campaigns and educational programs can help individuals and households understand the importance of waste reduction, segregation, and recycling. Citizens can be encouraged to adopt sustainable waste management practices through incentives, such as reduced waste collection fees for households that recycle or compost effectively. Engaging communities in the waste management process fosters a sense of responsibility and ownership, leading to increased participation and compliance with waste management guidelines.
In addition to environmental benefits, efficient waste management and recycling practices also offer economic opportunities. The recycling industry can create jobs and stimulate local economies through the collection, processing, and manufacturing of recycled materials. By promoting a circular economy, where waste is viewed as a valuable resource, cities can contribute to the creation of a sustainable and resilient economy.
Furthermore, sustainable waste management practices contribute to the overall cleanliness and aesthetic appeal of cities. Proper waste collection and disposal systems help maintain cleanliness, reduce litter, and prevent the spread of diseases. A clean and well-managed waste management system enhances the livability of cities, attracting visitors and fostering a sense of pride among residents.
Effective waste management and recycling practices are essential for achieving sustainable cities and communities. Goal 11 emphasizes the adoption of integrated waste management systems that prioritize waste reduction, recycling, and resource recovery. By implementing waste reduction strategies, promoting waste segregation, establishing recycling facilities, and promoting composting, cities can minimize the environmental impact of waste, conserve resources, and promote a circular economy. Public education and community engagement play a crucial role in ensuring the success of sustainable waste management initiatives. By investing in sustainable waste management practices, cities can create cleaner, healthier, and more environmentally-friendly urban environments for present and future generations
Climate Resilience
Building climate resilience is a critical aspect of creating sustainable cities and communities. With the increasing impacts of climate change, such as rising temperatures, extreme weather events, and sea-level rise, it is crucial for cities to develop adaptation and mitigation strategies to reduce vulnerability and enhance resilience. Goal 11 of the Sustainable Development Goals recognizes the importance of incorporating climate resilience into urban planning and development.
One of the key objectives of Goal 11 is to improve infrastructure resilience. This involves designing and constructing infrastructure that can withstand the impacts of climate change. For example, in coastal areas, infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and buildings can be built to be more resistant to storm surges and sea-level rise. In areas prone to extreme heat, infrastructure can incorporate heat-resistant materials and design elements that promote natural ventilation and cooling. By integrating climate resilience into infrastructure planning and development, cities can ensure that their critical systems and services remain operational during and after climate-related events, reducing disruption and protecting the well-being of their populations.
Implementing early warning systems is another important strategy for climate resilience. Early warning systems help cities anticipate and respond to climate-related hazards, such as hurricanes, floods, and heatwaves. These systems involve monitoring weather patterns and environmental conditions, as well as disseminating timely and accurate information to residents and relevant authorities. By providing early warnings, cities can improve preparedness, facilitate timely evacuations if necessary, and minimize the potential impacts of climate-related events on human lives and infrastructure.
Creating green infrastructure is another crucial measure for climate resilience. Green infrastructure refers to the use of natural elements, such as parks, urban forests, green roofs, and permeable surfaces, to manage stormwater, reduce the urban heat island effect, and enhance biodiversity. Green infrastructure helps mitigate the impacts of climate change by absorbing and storing rainwater, reducing the risk of flooding, and providing shade and cooling effects in urban areas. By incorporating green spaces into cities and communities, not only can the negative impacts of urbanization be mitigated, but residents can also enjoy improved air quality, enhanced recreational opportunities, and a better overall quality of life.
In addition to these specific strategies, incorporating climate resilience into urban planning is crucial. Cities need to consider climate risks and vulnerabilities in their long-term development plans. This includes identifying areas at risk of flooding, landslides, or other climate-related hazards and implementing appropriate land-use planning measures. For example, zoning regulations can be updated to prevent construction in high-risk areas or require developers to implement climate adaptation measures in their projects. By integrating climate resilience into urban planning, cities can ensure that new developments are designed with climate change in mind and that existing infrastructure is retrofitted to enhance resilience.
Furthermore, collaboration and partnerships are essential for building climate resilience. Cities should work with various stakeholders, including government agencies, community organizations, businesses, and academia, to develop and implement climate adaptation and mitigation strategies. Collaboration allows for the sharing of knowledge, expertise, and resources, leading to more effective and comprehensive climate resilience measures. Engaging the community in the planning and decision-making process also fosters a sense of ownership and increases the likelihood of successful implementation.
Investing in climate resilience not only helps cities adapt to the impacts of climate change but also brings multiple co-benefits. For example, green infrastructure not only helps manage stormwater but also improves air quality, enhances urban biodiversity, and provides recreational spaces for residents. Climate-resilient infrastructure can also contribute to energy efficiency, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainability.
In conclusion, building climate resilience is a crucial component of Goal 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities. By incorporating climate resilience into urban planning, improving infrastructure resilience, implementing early warning systems, and creating green infrastructure, cities can reduce vulnerability and enhance their ability to withstand the impacts of climate change. Collaboration and community engagement are vital for the successful implementation of climate resilience measures. By investing in climate resilience, cities can protect their populations, infrastructure, and natural resources, ensuring a more sustainable and resilient future for all.
Preserving Cultural Heritage
Preserving cultural heritage is a vital aspect of sustainable development, and Goal 11 of the Sustainable Development Goals emphasizes the significance of safeguarding cultural heritage sites, historic buildings, and traditional practices. Cultural heritage encompasses a wide range of tangible and intangible elements, including monuments, archaeological sites, traditional craftsmanship, folklore, language, and social practices. By protecting and promoting cultural heritage, cities and communities can foster a sense of identity, promote social cohesion, attract tourism, and generate economic opportunities.
One of the key objectives of Goal 11 is to safeguard cultural heritage sites and historic buildings. These sites hold significant historical, architectural, and cultural value, and their preservation is crucial for maintaining a connection to the past and passing on knowledge to future generations. Historic buildings are not only physical structures but also bear witness to the stories, traditions, and identity of a place and its people. By protecting and conserving these sites, cities can maintain their unique character and cultural identity, contributing to a sense of pride and belonging among residents.
Preserving cultural heritage also has economic benefits for cities and communities. Cultural heritage tourism has gained prominence in recent years, with travelers seeking authentic experiences and a deeper understanding of local cultures. By promoting and preserving cultural heritage sites, cities can attract tourists, generate revenue, and create employment opportunities. Local businesses, such as hotels, restaurants, and handicrafts, can thrive through the promotion of cultural tourism, contributing to the local economy and livelihoods. Additionally, cultural heritage preservation can revitalize historic districts and neighborhoods, attracting investment and fostering sustainable economic growth.
Furthermore, the preservation of cultural heritage contributes to the social fabric of cities and communities. Cultural heritage is often intertwined with people's identities, traditions, and sense of belonging. By safeguarding cultural heritage, cities can strengthen social cohesion, promote intergenerational dialogue, and foster community pride. Cultural heritage preservation provides opportunities for communities to celebrate and showcase their traditions, customs, and artistic expressions. This engagement with cultural heritage enhances social inclusion and diversity, creating spaces for dialogue, mutual understanding, and appreciation of different cultures and perspectives.
In addition to tangible cultural heritage, Goal 11 also recognizes the importance of preserving intangible cultural heritage. Intangible cultural heritage refers to practices, expressions, knowledge, and skills that are passed down from generation to generation. It includes oral traditions, performing arts, rituals, traditional craftsmanship, and knowledge systems. Preserving intangible cultural heritage not only safeguards traditional practices but also promotes cultural diversity and encourages intercultural dialogue. It is through the transmission and revitalization of intangible cultural heritage that cities and communities can maintain their unique identities and contribute to a rich and vibrant cultural landscape.
To effectively preserve cultural heritage, cities and communities need to engage in comprehensive and inclusive planning and decision-making processes. This involves collaboration with local communities, cultural institutions, heritage experts, and relevant stakeholders. It is important to involve local residents in decision-making processes, ensuring that their voices are heard and their cultural heritage is respected and protected. Additionally, capacity-building initiatives and educational programs can empower local communities to actively participate in the preservation and promotion of their cultural heritage.
The preservation of cultural heritage is an integral part of sustainable development. Goal 11 highlights the importance of safeguarding cultural heritage sites, historic buildings, and traditional practices. By protecting and promoting cultural heritage, cities and communities can foster a sense of identity, social cohesion, and economic opportunities. Cultural heritage preservation contributes to the uniqueness and vibrancy of cities, attracting tourism, and enriching the lives of residents. By integrating cultural heritage into urban planning and development, cities can create sustainable, inclusive, and culturally rich environments for present and future generations.
Conclusion
Goal 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities is a critical component of the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals. As urbanization continues to accelerate, it is crucial to prioritize sustainable urban planning, green infrastructure, affordable housing, sustainable transport systems, waste management, climate resilience, and the preservation of cultural heritage. By working towards these objectives, cities and communities can create a more sustainable, inclusive, and livable future for all. Embracing Goal 11 is not only an environmental imperative but also a pathway to economic prosperity, social equity, and a greener future for generations to come.
#How to create sustainable cities and communities#Importance of sustainable urban planning#Achieving Goal 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities#Benefits of green infrastructure in cities#Affordable housing solutions for sustainable communities#Promoting sustainable transport systems in cities#Effective waste management for sustainable cities#Preserving cultural heritage in sustainable development#Building climate resilience in cities#The role of recycling in sustainable cities#Sustainable urban planning for resilient communities#Creating inclusive and safe cities through Goal 11#How green spaces enhance sustainable cities#Addressing the challenges of affordable housing in urban areas#Reducing carbon emissions through sustainable transport#Implementing waste reduction strategies for sustainable communities#The economic benefits of cultural heritage preservation#Enhancing infrastructure resilience in the face of climate change#Sustainable waste management practices for cities#Promoting community engagement in sustainable urban development#Integrating climate resilience into urban planning#Incorporating green infrastructure for sustainable communities#The social impact of affordable housing initiatives#Mitigating air pollution through sustainable transport systems#Circular economy approaches in waste management for cities#Preserving historic buildings for sustainable cities#Creating resilient communities through Goal 11 strategies#Promoting cultural diversity in sustainable urban environments#Building sustainable cities for future generations#Achieving sustainability goals through Goal 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
0 notes
Text
youtube
Bringing "Balloons Over Broadway" to Life - A Live Camera Project in Green Screen by DoInk
In the enchanting world of children's literature, "Balloons Over Broadway" by Melissa Sweet is a beloved tale that unfolds during the Macy's Thanksgiving Day Parade. You can make the story come to life with the magic of green screen technology. In this video tutorial blog post, we'll guide you through the process of creating a Live Camera Project in Green Screen by DoInk, where you can integrate your students, their balloons or both into the pages of "Balloons Over Broadway" and let their imagination take flight.
By combining the magic of the Green Screen by DoInk app with the enchanting pages of "Balloons Over Broadway," you can create an immersive experience that brings the story to life. Whether you're a teacher looking to engage your students or a storyteller aiming to captivate your audience, this project opens up a world of creative possibilities. Step into the pages of "Balloons Over Broadway" and let your imagination soar like the parade balloons themselves.
#[A] versatile#easy-to-use movie maker yields great results#Chroma Key#Balloons Over Broadway#Default (GPT-3.5)#User#Brainstorm 5 episode ideas for my new podcast on urban design.#ChatGPT#Certainly! Here are five episode ideas for your podcast on urban design:#“The Evolution of City Planning: From Ancient Times to Modern Metropolises”#In this episode#explore the history of urban design#tracing the development of cities from ancient civilizations to contemporary urban landscapes. Discuss key milestones#influential architects#and how historical urban planning concepts still impact cities today.#“Sustainable Cities: Innovations in Green Urban Design”#Dive into the world of sustainable urban design and its importance in combating climate change. Feature interviews with urban planners#architects#and sustainability experts to discuss green building practices#renewable energy solutions#and sustainable transportation initiatives in cities worldwide.#“The Future of Urban Mobility: Smart Cities and Transportation Trends”#Explore the intersection of urban design and transportation. Discuss the rise of smart cities#advancements in public transit#the impact of autonomous vehicles#and how technology is shaping the way we move within urban environments.#“Urban Renewal and Gentrification: Balancing Development and Community Preservation”#Del#Check out our new Green Screen Tutorial on how to make a photo in Green Screen by Doink#I'm sorry for any confusion
0 notes
Photo
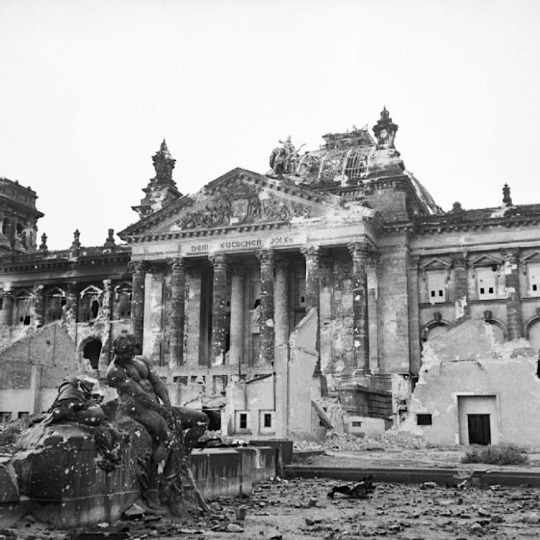

The Bombing of Berlin
The bombing of Berlin, aka the Berlin Air Offensive or Battle of Berlin (Air), was a sustained bombing campaign on the German capital by the British Royal Air Force and United States Air Force from November 1943 until March 1944. The objective, which failed, was to bomb Germany into surrender and win WWII without the necessity of land operations.
Area Bombing
The commander-in-chief of the RAF Bomber Command, Arthur Harris (1892-1984), had received backing at the highest level for the night-time area bombing (aka carpet bombing) of German industrial targets and industrial cities. The Royal Air Force (RAF) and United States Army Air Force (USAAF) had already conducted a Combined Bomber Offensive and made repeated attacks on the Ruhr industrial area of Germany (Battle of the Ruhr, March-July 1943) and on Hamburg with the utterly devastating Operation Gomorrah (July-August 1943). Typically, the RAF bombed by night and the USAAF by day in these combined operations. As Winston Churchill (l. 1874-1965), the British prime minister put it:
We shall bomb Germany by day as well as by night in ever-increasing measure, casting upon them month by month a heavier discharge of bombs, and making the German people taste and gulp each month a sharper dose of the miseries they have showered upon mankind.
(Liddell Hart, 189)
By the summer of 1943, the Allied leaders began to shift their focus to a future invasion of Continental Europe. The Allies issued the Pointblank Directive in June 1943, which stated that bombing raids in Europe should prioritise Germany's capacity to produce fighter planes, which could be used against ground troops in the D-Day Normandy landings (Operation Overlord) planned for the following summer. Air supremacy had to be achieved before Overlord could get underway. However, Harris remained sceptical of the possibility of hitting small but strategically important targets like weapons factories. This was in some way born out by the USAAF's Schweinfurt-Regensburg raids. The first Schweinfurt raid in August 1943 had not been very successful in damaging the crucial ball-bearing factories, and many aircraft had been lost in the process. (The USAAF returned to Schweinfurt and was more successful in October). Berlin did have key armaments factories, and these could be knocked out with a wider and more indiscriminate bomb-dropping strategy, Harris thought. Berlin was also an obvious transport hub and, of course, a prestige target, too. Harris believed that the heavy bombing of Berlin could ultimately lead to Germany's surrender and so the Allies might even avoid the necessity of dangerous and time-consuming land operations.
There were some flaws in the plan. Berlin was a much bigger city than those bombed previously and so would take many more raids to damage. Harris knew this, and so he called for a force of 6,000 bombers, but this was never possible; the RAF and USAAF combined only had some 3,000 bomber planes at any one time. Berlin was also well-defended with over 100 anti-aircraft batteries. The historian M. Hastings describes Berlin as "the largest and most heavily defended industrial urban area in Europe" (285). As the historian R. Neillands put it, Berlin "was always a difficult target. It lay a long way into Germany, close to the eastern frontier, and was a very big and very flat city, with few physical features…" (217).
Another problem was that in 1943, Allied fighter planes still did not have sufficient fuel range to escort bombers to targets deep in Germany. Finally, the other bombing campaigns, which included the thousand-bomber raid on Cologne in 1942, had not shattered civilian morale despite causing enormous casualties and damage. This had also been true of the German bombing of British cities and the London Blitz earlier in the war. Even if German civilian morale could be broken, in a totalitarian state built on violence, there was probably not much civilians could do to influence policy change anyway. Despite these pitfalls, the Combined Chiefs of Staff gave Harris the green light, and the bombers were sent to Berlin. Crucially, the USAAF, preferring to pursue its own targets like Germany's oil supplies, would not join the raids until near the end of the campaign. The RAF bomber crews would be on their own in their effort to bomb into submission the city they called "Big B".
Continue reading...
66 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Williamsburg Bridge remains a beloved and functional part of New York City's infrastructure, offering more than just a physical connection between boroughs. It weaves together the social, cultural, and economic fabric of the city while serving as a reminder of the city's enduring spirit and resilience.
Accessibility for Bicyclists: In recent years, the Williamsburg Bridge has become increasingly popular among cyclists. The addition of dedicated bike lanes and paths has made it a key route for those commuting between Brooklyn and Manhattan by bicycle. This has contributed to the city's efforts to promote sustainable transportation options.
Emergency Services: The Williamsburg Bridge, like other major bridges in New York City, is equipped with emergency evacuation plans and protocols. It is considered an essential route for emergency vehicles and personnel during crises or natural disasters.
Cultural Influence: Beyond its practical role, the Williamsburg Bridge has had a profound cultural influence, particularly in the Brooklyn neighborhood it connects to. Williamsburg, with its vibrant arts scene, has become synonymous with the bridge's name, and it has featured prominently in local art, music, and literature.
In Popular Culture: The Williamsburg Bridge has appeared in numerous movies, TV shows, and music videos. Its distinctive architecture and picturesque views have made it a favorite location for filmmakers and artists looking to capture the essence of New York City.
Connecting Diverse Communities: The bridge has played a crucial role in connecting diverse communities in Manhattan and Brooklyn. It has been a conduit for the exchange of cultural influences, economic activity, and social interactions.
Historical Preservation and Restoration: Various organizations and government agencies have been involved in preserving and restoring the bridge to ensure its longevity. Efforts have included repainting the bridge, restoring its architectural features, and maintaining its structural integrity.
Design Features: The Williamsburg Bridge's towers are constructed of steel, and its suspension cables are made of wire rope. The bridge's overall design showcases elements of the Beaux-Arts architectural style, with ornamental details and decorative flourishes.
Maintenance Challenges: Maintaining a bridge of this size and age is an ongoing challenge. The bridge requires regular inspections, repairs, and upgrades to keep up with modern safety standards and the demands of urban transportation.
Future Developments: As New York City continues to evolve, the Williamsburg Bridge remains a vital part of the city's infrastructure. Future developments and improvements may include further enhancements to pedestrian and cyclist facilities, as well as ongoing efforts to reduce environmental impacts.
Centennial Celebrations: The Williamsburg Bridge celebrated its centennial in 2003 with various events and activities to mark its 100th anniversary. This milestone offered an opportunity for New Yorkers to reflect on the bridge's historical importance.
Artistic Expressions: Over the years, the Williamsburg Bridge has been a canvas for artistic expressions. Street art and graffiti have adorned its support structures and pedestrian walkways, contributing to the bridge's cultural identity.
Traffic Congestion and Alternatives: Like many urban bridges, the Williamsburg Bridge experiences traffic congestion during peak hours. This congestion has prompted discussions about transportation alternatives, such as improved public transit options, to ease the burden on the bridge and reduce environmental impacts.
Hurricane Sandy and Resilience: The bridge, like other infrastructure in New York City, faced significant challenges during Hurricane Sandy in 2012. The storm surge resulted in flooding and temporary closures. In response, the city has explored ways to enhance the resilience of critical infrastructure, including the Williamsburg Bridge, to future extreme weather events.
Iconic Landmark: The Williamsburg Bridge is not just a transportation link but also an iconic symbol of New York City's skyline. Its unique silhouette and the way it frames views of the city have made it a subject of admiration for photographers, artists, and tourists alike.
Community Engagement: The Williamsburg Bridge has been the focus of community engagement and activism. Local residents and organizations have advocated for improvements, safety measures, and the preservation of its historical and cultural significance.
Economic Impact: The bridge's role in connecting Manhattan and Brooklyn has had a significant economic impact on both boroughs. It has facilitated the movement of goods and people, supporting businesses and industries on both sides of the East River.
Night Illumination: The Williamsburg Bridge is often illuminated at night, casting a stunning glow over the East River. The changing colors and lighting schemes have been used to mark special occasions and holidays, enhancing the bridge's visual appeal.
Symbol of Progress: Throughout its history, the Williamsburg Bridge has symbolized progress, connectivity, and the spirit of innovation. It reflects the dynamism of New York City as it continues to evolve and adapt to the needs of its residents.
The Williamsburg Bridge stands as a testament to both engineering innovation and the enduring cultural significance of infrastructure in urban life. It has served as a lifeline for generations of New Yorkers, connecting people, neighborhoods, and opportunities across the East River.
<Previous page - Williamsburg Bridge - Next page>
#Williamsburg Bridge#Bridge#Brooklyn#new york city#new york#new-york#newyork#manhattan#nyc#ny#urban#city#usa#United States#buildings#travel#journey#outdoors#street#architecture#visit-new-york.tumblr.com
230 notes
·
View notes
Note
Re zoning regulation reform: could you go into detail as what that would look like in terms of wiping the slate clean. I feel like it would be better to go the houston route and just be zoning free
You do not want to go the Houston route.
youtube
Houston may claim to be "zoning-free" - and to be fair, it doesn't have some of the more common regulations on land use, or density, or height restrictions (more on this in a minute) - but the reality is far more complicated and the status quo is not one that's friendly to the interests of working-class and poor residents, or to the possibility of sustainable urbanism.
The answer to NIMBYism isn't to abolish all regulations and let the free market rip, it's to surgically target zoning, planning, and litigation that is used against affordable housing, public/social housing, mass transit, clean energy, and walkable neighborhoods, and to replace it with new forms of regulation that encourage these forms of development.
So let's take take these categories in order.
Zoning
As I tell my Urban Studies students, zoning is both one of the most subtle and yet comprehensive ways in which the state shapes the urban environment - but historically it has been used almost exclusively in the interests of racism and classism. Reforming zoning requires going over the code with a fine-toothed comb to single out all the many ways in which zoning is used to make affordable housing impossible:
The most important one to tackle first is density zoning and building heights limitations. The former directly limits how many buildings you can have per unit of land (usually per acre), while the latter limits how big the buildings can be (expressed either as the number of stories or the number of feet, or as both). Closely associated with these zoning regulations are minimum lot size regulations (which regulate how much land each individual parcel of real estate has to cover, and thus how many how many housing units can be built in a given area), and lot coverage, setbacks, and minimum yard requirements (which limit how much square footage of a lot can be built on, and what kinds of structures you can build).
the other big one is use zoning. To begin with, we need to phase out "single use" zoning that designates certain areas as exclusively residential or commercial or industrial (a major factor that drives car-centric development, makes walkable neighborhoods impossible, and discourages the "insula" style apartment building that has been the core of urbanism since Ancient Rome) in favor of "mixed use" zoning that allows for neighborhoods that combine residential and commercial uses. Equally importantly, we need to eliminate single-family zoning and adopt zoning rules that allow for a mix of different kinds of housing (ADUs, duplexes and triplexes, rowhouses/terraced houses, apartment buildings).
finally, the most insidious zoning requirements are seemingly incidental regulations. For example, mandatory parking minimums not only prioitize car-dependent versus transit-oriented development but also eat up huge amounts of space per lot. The most nakedly classist is "unrelated persons" zoning, which is used to prevent poorer people from subdividing houses into apartments, which zaps young people who are looking to be roommates and older people looking to finance their retirements by running boarding houses or taking in lodgers, as well as landlords looking to convert houses from owner-occupied to rental properties.
So I would argue that the goal of reform should be not to eliminate zoning, but rather to establish model zoning codes that have been stripped of the historical legacies of racism and classism.
Planning
Similar to how zoning shouldn't be abolished but reformed, the correct approach to planning isn't to abolish planning departments wholesale, but to streamline the planning process - because the problem is that right now the planning process is too slow, which raises the costs of all kinds of development (we're focusing on housing right now, but the same holds true for clean energy projects), and it allows NIMBY groups to abuse the public hearings and environmental review process to block projects that are good for the environment and working-class and poor people but bad for affluent homeowners.
As those Ezra Klein interviews indicate, this is beginning to change due to a combination of reforms at both the state and federal level to speed up the CEQA and EPA environmental review process in a number of ways. For example, one change that's being made is to require planning agencies and environmental agencies to report on the environmental impact of not doing a project as well, to shift the discussion away from petty complaints about noise and traffic and "neighborhood character" (i.e, coded racism and classism) and towards real discussions of social and environmental justice.
At the same time, more is needed - especially to reform the public hearing process. While originally intended by Jane Jacobs and other activists in the 1970s as a democratic reform that would give local communities a voice in the planning process, "participatory planning" has become a way for special interests to exercise an unaccountable veto power over development. Because younger, poorer and more working class, and communities of color often don't have time to attend public hearing sessions during the workday, these meetings become dominated by older, whiter, and richer residents who claim to speak for the whole of the community.
Moreover, because community boards are appointed rather than elected and public hearings operate on a first-come-first-serve basis, an unrepresentative minority can create a false impression of community opposition by "stacking the mike" and dialing up their level of militancy and aggression in the face of elected officials and civil servants who want to avoid controversy. (It's a classic case of diffuse versus concentrated interests, something that I spend a lot of classroom time making sure that my students learn.)
Again, the point shouldn't be to eliminate public hearings and other forms of participatory planning, but to reform them so that they're more representative (shifting public hearings to weekends and allowing people to comment via Zoom and other online forums, conducting surveys of community opinion, using a progressive stack and requiring equal time between pro and anti speakers, etc.) and to streamline the review process for model projects in categories like affordable housing, clean energy, mass transit, etc.
Litigation
Alongside the main planning process, there is also a need to reform the litigation process around development. In addition to traditional tort lawsuits from property owners claiming damage to their property from development, a lot of planning and environemntal legislation allows for private groups to sue over a host of issues - whether the agency followed the correct procedures, whether it took into account concerns about this impact or that impact, and so forth.
As we saw with the case of Berkeley NIMBYs who used CEQA to block student housing projects over environmental impacts around "noise," this process can be used to either block projects outright, or even if the NIMBYs eventually lose in court, to draw out the process until projects fall apart due to lack of funding or the proponents simply lose their patience and give up.
This is why we're starting to see significant reforms to both state and federal legislation to streamline the litigation process. The categorical exemptions from review that I discussed above also have implications for litigation - you can't sue over reviews that didn't happen - but there are also efforts to speed up the litigation process through reducing what counts as "administrative record" or by putting a nine-month cap on court proceedings.
Again, this is an area where you have to be very surgical in your changes. Especially when the politics of the issue divide environmental groups and create odd coalitions between labor, business, climate change activists, and anti-regulation conservatives, you have to be careful that the changes you are making benefit affordable housing, clean energy, mass transit and the like, not oil pipelines and suburban sprawl.
#public policy#housing#zoning#policy history#urban planning#public housing#social housing#yimbys#yimbyism#affordable housing#urban studies#urbanism#houston#nimbyism#nimbys#environment#climate change#clean energy
95 notes
·
View notes
Text
Julius Scott’s legendary study tells [...] of the unrest of “masterless” communities, as he terms them, in the late eighteenth-century Caribbean and its implications for the Atlantic World. This unrest was undergirded by what he terms a “common wind” of seditious political news circulating through an increasingly mobile and interconnected region. He deftly sets the context [...] to imperial tensions that culminated in uprisings and revolutions within [...] the French, British, and Spanish Empires. [...] He builds what is this field-defining work from a triangulated analysis of three central hubs of the colonial Caribbean in terms of [...] prosperity in the plantation economy, and political importance to these aforementioned empires: Saint-Domingue [Haiti], Jamaica, and Cuba. But he also explores similar occurrences within [...] Martinique and Guadeloupe for the French, Venezuela and Trinidad for the Spanish, and Dominica and Grenada for the British. He also includes [...] the engagement of the newly formed United States in this network, reinforcing the broader Atlantic impact of the common wind’s radical currents.
---
Chapter 1 explores the upheaval afoot in the mid-1700s colonial Caribbean through a closer look at the movements of a range of actors including enslaved runaways, military deserters, contraband smugglers, free people of color, and poor whites hustling in the islands’ urban centers and surrounding countrysides.
A variety of settings - including the fringes of plantations, maroon settlements, town-based markets, taverns, hospitals, barracks, and wharves - might presumably, if read with the archival grain, illuminate the map of state control. Instead, in Scott’s analysis, these represent the contours of the working class’s unlawful movements and ultimately their fraying of the colonial order, anticipating what Stephanie M. H. Camp [...] would aptly name [...] the “rival geography” of slave society.
---
Chapter 2 shows how sailors’ illicit forms of mobility [...] blurred the bounds between land and sea in this narrative of popular dissent. Their movements [...] as social beings and political dissidents bled into and helped sustain similar kinds of illicit commerce and socializing [...]. Chapters 3 and 4 demonstrate how the common wind consistently blew subversive ideas into and around the Caribbean, much to officials’ chagrin. Scott here homes in on the politically volatile era from the late 1770s through the late 1790s, which saw declarations of war, drastic changes in slavery policy [...] and the emergence of U.S., French, and, most significantly, Haitian revolutionary uprising. [...] [E]nslaved communities everywhere in the region followed as intently as they could as the campaign of the enslaved rebels in Saint-Domingue began in 1791. [...] Political news, no matter how hard officials in the colonies and the metropoles tried to block it, spilled into all levels of society [...]. What flowed through all of these channels animated questions about master-slave relations, mercantilist policy, individual rights [...]. Scott carefully traces the influence of the unfolding Haitian Revolution on well-planned but eventually thwarted uprisings of enslaved people in the Venezuelan port city Coro, the Dutch colony of Curaçao, and the parish of Pointe Coupee in then Spanish Louisiana, all in 1795. He also illuminates the multiple instances of inspiration in the 1790s evidenced in enslaved communities throughout the United States [...].
---
Essentially Scott reveals that the Age of Revolutions cannot be understood without comprehending black resistance in times of war and peace. The tale of Phebe, one of many enslaved Jamaican female runaways who became an itinerant higgler hiding in plain sight in urban spaces like Kingston, or the story of the 1790 mutiny of four enslaved sailors who overtook the Saint Kitts sloop the Nancy with respective origins in the Caribbean, West Africa, and the U.S. South, which Scott called a “microcosm” of the Atlantic, are but two of multiple narratives he includes to show that enslaved people [...] actively built and sustained those circuits via their multilingualism, their savvy, and above all their dedication to achieving a state of masterlessness [...].
This could be achieved not just through formal manumission processes, but through running away and re-creating new lives and livelihoods [...]. The [...] knowledge that these dissidents obtained in their labors allowed them to escape to lives not “off the grid,” but rather in the centers of commercial and state activity, ensconced in communities of opposition and poised to obtain news that prepared them well for their next moves in their albeit precarious existence. [...]
Scott complicates earlier framings of the oppositional working class as strictly of European origin [...]; [...] Scott’s unpublished dissertation [...] influenced the interventions made in Linebaugh and Rediker’s The Many-Headed Hydra [...] years later. [...] He centers enslaved people within the revolutionary Atlantic not just as workers [...] but also as strategic thinkers, and he does so long before it was popular to do so in this field of history. [...] [H]e demonstrates how so many ordinary enslaved women and men regularly engaged in quotidian forms of fugitivity across various imperial territories of the Caribbean [...]. The dissertation also came several years in advance of the still pivotal call advanced by Michel-Rolph Trouillot’s 1995 Silencing the Past, about the denied centrality of the Haitian Revolution to the Age of Revolutions in its time and in retrospect. Scott’s work undeniably influenced many Atlantic historians [...]; it is also a genuinely exciting read.
---
All text above by: Natasha Lightfoot. "The Common Wind: A Masterful Study of the Masterless Revolutionary Atlantic". The American Historical Review, Volume 125, Issue 3, pages 926-930. June 2020. At: doi dot org slash 10.1093/ahr/rhaa230 [Bold emphasis and some paragraph breaks/contractions added by me. Presented here for commentary, teaching, criticism purposes.]
#abolition#tidalectics#caribbean#debt and debt colonies#opacity and refusal and fugitivity#multispecies#ecologies#geographic imaginaries
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Discover Modern Living at Windlass River Valley: The Premier Apartments in Dehradun

Nestled in the serene foothills of the Himalayas, Dehradun has emerged as a top destination for those seeking a blend of urban convenience and natural beauty. Among the many residential developments in this picturesque city, Windlass River Valley stands out as a premier choice for those looking for apartments in Dehradun. This sprawling township offers a lifestyle that combines modern amenities with the tranquility of nature, making it an ideal home for families, professionals, and retirees alike.
The Appeal of Dehradun
Dehradun’s charm lies in its unique combination of natural beauty and modern infrastructure. Known for its pleasant climate, lush greenery, and proximity to the mountains, Dehradun has always been a sought-after location for those seeking a peaceful lifestyle. Over the years, the city has also developed a robust infrastructure, with excellent educational institutions, healthcare facilities, and shopping centers, making it a perfect place for modern living.
For those considering an investment in real estate, particularly in apartments in Dehradun, the city offers a promising future. With its growing economy, improving infrastructure, and the increasing influx of professionals and retirees, Dehradun is quickly becoming a real estate hotspot. And within this burgeoning market, Windlass River Valley shines as a prime option for residential living.
Why Choose Windlass River Valley?
Windlass River Valley is more than just a residential project; it’s a well-planned township designed to offer a holistic living experience. Located in Harrawala, one of the city’s most rapidly developing areas, this township is strategically positioned to provide easy access to all of Dehradun’s key locations, while still offering the peace and quiet of suburban life.
1. Modern and Spacious Apartments
The apartments in Windlass River Valley are designed with modern lifestyles in mind. They feature spacious layouts with high-quality finishes, ensuring that residents enjoy both comfort and style. Whether you are looking for a cozy 2BHK or a more expansive 3BHK apartment, you’ll find a range of options that cater to different needs and preferences. Large balconies offer stunning views of the surrounding greenery, allowing you to enjoy the beauty of Dehradun right from your home.
2. World-Class Amenities
Windlass River Valley boasts a range of world-class amenities that cater to all aspects of modern living. Residents can enjoy a state-of-the-art clubhouse, swimming pools, fitness centers, and sports facilities, ensuring that there’s always something to do without leaving the township. For families, the well-designed play areas and parks provide safe and enjoyable spaces for children to play and explore.
3. Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Living
In today’s world, sustainable living is more important than ever. Windlass River Valley has been designed with eco-friendliness in mind. The township features green spaces, energy-efficient buildings, and waste management systems that minimize environmental impact. Living here means you can enjoy the best of modern amenities while also contributing to a sustainable future.
4. Security and Peace of Mind
Security is a top priority at Windlass River Valley. The township is equipped with 24/7 security systems, including CCTV surveillance and gated entry points, ensuring that residents feel safe and secure at all times. This focus on safety makes it an ideal choice for families and retirees who prioritize peace of mind.
5. Community Living
One of the standout features of Windlass River Valley is its focus on fostering a strong sense of community. The township is home to a diverse group of residents, creating a vibrant and inclusive community. Regular events and activities are organized within the township, encouraging residents to connect and build lasting relationships with their neighbors.
Investment Potential
Investing in an apartment in Dehradun, particularly at Windlass River Valley, offers excellent long-term potential. Dehradun’s real estate market is on the rise, with property values steadily increasing as the city continues to develop. By choosing to invest in Windlass River Valley, you’re not just buying a home; you’re securing a valuable asset that is likely to appreciate over time.
Furthermore, Dehradun’s growing popularity as a destination for both tourism and retirement means that there is a strong demand for quality housing. Whether you plan to live in your apartment or rent it out, you can expect a good return on your investment.
The Windlass River Valley Lifestyle
Living at Windlass River Valley means embracing a lifestyle that balances convenience, luxury, and natural beauty. Imagine waking up to the sight of the majestic Himalayas, spending your evenings strolling through beautifully landscaped gardens, and having all the amenities you need just a short walk away. This is the lifestyle that Windlass River Valley offers—a perfect blend of urban and suburban living.
For those who work in Dehradun or nearby cities, the township’s location ensures that commuting is hassle-free. Major roads and public transportation are easily accessible, making it convenient to travel to and from the city. At the same time, the peaceful surroundings offer a welcome escape from the hustle and bustle of city life.
If you’re in the market for apartments in Dehradun, Windlass River Valley should be at the top of your list. With its modern design, comprehensive amenities, and prime location, it offers everything you need for a comfortable and fulfilling life. Whether you’re looking to invest in real estate or find your dream home, Windlass River Valley is a choice you won’t regret.
Explore the possibilities today and discover why Windlass River Valley is the premier destination for modern living in Dehradun.
#DehradunLiving#ApartmentsInDehradun#WindlassRiverValley#LuxuryLiving#DehradunRealEstate#ModernHomes#EcoFriendlyLiving#DehradunLifestyle#UrbanLiving#DreamHome#ResidentialProjects#HimalayanLiving#InvestInDehradun#CommunityLiving#SustainableHomes#apartment#dehradun#wrv#flats#township#smarttownship#apartments in dehradun#home
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
While Marx often shows enthusiasm for the potentiality of enhanced forms of human cooperation enabled by globalizing production, already in the nineteenth century, he observed an antagonistic separation of town and country and suggested that production chains were overstretched and wasting resources. Today, lessening the spatial disjuncture between production and consumption must be an explicit feature and aim of sustainable and just transition and, in this context, calls on the left for partial deglobalization, including the shortening of commodity chains, have merit and are quite consistent with Marx’s analysis. In a process of partial deglobalization, production for local and domestic needs—rather than production for export—would again become the center of gravity of the economy. A move away from the export orientation of domestic corporations and a process of renationalization could also allow enterprises to begin to develop their own strategies, moving away from the whims of the global market and choices taken by corporate controllers. Such transformation could enable spaces for independent development in the Global South. To do so, they could focus on shifting agrarian systems, orienting their production away from agro-export (which is a source of tremendous ecological irrationality and unequal exchange) toward food sovereignty. Such shifts would need to be accompanied by simultaneous, coordinated shifts toward enhanced local and domestic food production in Global North, alongside a move from high-input agriculture to agroecology, and, in settler colonial contexts, enhanced Indigenous sovereignty. Within domestic spaces or regions, efforts must simultaneously be made to mend a rift between the city and the country. For a model of the environmentalist city, one could look to Havana for inspiration. During Cuba’s Special Period in the 1990s, organic, low-input agriculture was developed both in the countryside, as well as in the island’s capital through urban farms. Urban agriculture is here not niche or small-scale—it covers large expanses within and at the outskirts of the city, where rich land is located. In the transition to renewables, energy production should also be localized as much as possible. This is a potentiality inherent in renewable energy “flow,” in contrast to concentrated energy “stock,” or fossil fuels. While lessening the spatial disjuncture between production and consumption is part of developing ecologically rational production, this aim should be recognized to be in some tension with economic planning (at least in the longer term), insofar as expansive planning is potentiated by the socialization of production. Thus, calls for localization of production imply a diminishment in productive association across firms and regions and the potential to plan such interconnections. Practically, it is important to recognize that such a process confronts material interdependencies, as existing productive networks and infrastructural configurations support and sustain huge swaths of human life. Different regions and cities also have different specializations and different ecological capacities. In an existing world of evolved economic interdependencies, the reproductive needs of various communities require continued global resource flows. Climate change also creates severe survival and livelihood challenges on a highly uneven basis, and global trade and divisions of labor can act as safeguards against issues such as pandemics related to water-supply failures and reduced agricultural yields. More broadly, we should carefully consider Marx’s suggestion that well-organized territorial divisions of labor are collective powers and can be a part of collaboration in human affairs. This extends to territorial specialization, which, consciously organized, could involve a collaborative partitioning of resources and capacities.
37 notes
·
View notes
Text


Dig For Victory!
Most people have a garden or could take on an allotment fairly near to where they live. Organising garden sharing schemes where people with gardens they can’t use team up with people who want to garden but don’t have gardens is a worthwhile step. We need to investigate ways of producing and distributing organic food in our localities in ways that maintain biodiversity and as far as possible outside the money economy. Think organic, low-impact farming won’t work? A recent study of sustainable agriculture using low-tech methods introduced on farms supporting 4m people in majority world countries revealed that food production increased 73%, crops like cassava and potato showed a 150% increase and even large ‘modern’ farms could increase production 46%. The future occupation and use of land will depend on the extent to which all who wish to do so have discussed and consented to such use, that those occupying or using the land continue to work in solidarity with the whole of society within broad principles of co-operation, sharing freely both the means of production and what is produced. No individual or group of individuals will have any ‘right’ to say “the land must be used in the way we decide” nor can what is on or under the land or produced upon it be their property, whether plant or animal. The number of people involved in agriculture (in its widest sense) will probably expand greatly, with vast estates and agri-corp holdings broken up and shared out but also urban farms created in and near towns. The aim of agriculture (and associated activities like food processing) will be self-sufficiency for the localities and specialization or growing for ‘export�� only where there is surplus land or productive forces. It is likely that neighbours, co-workers, communities and communes will collectively agree that land will be used in particular ways according to a plan or program of beneficial change. This will not always be in the direction of development or ‘efficiency’ (which will have different definitions and parameters anyway); if people need more gardens or wilderness, small-holdings instead of sheep stations, they will create them.
To many people this will sound utopian. However we believe that if this approach was developed widely – and applied to our other vital needs — it could subtly undermine the credibility and power of the global economy (as well as having obvious personal benefits in terms of health etc). It is an important part of building social solidarity and a community of resistance in majority world communities. It would be a way of showing our solidarity with these majority world movements based around issues of land use, access to resources and so on: communities of small farmers are organising seed banks to preserve crop diversity as well as launching more militant attacks on the multinationals such as trashing fields of GM cotton and destroying a Cargill seed factory. In the longer term as (hopefully) numbers and confidence increase, large long-term squats will become a possibility on land threatened by capitalist development either for roads, supermarkets, airports etc or for industrialised food production being taken back for subsistence food production and as havens of biodiversity. We should take inspiration from the Movimento Sem Terra in Brazil where in the face of severe state repression and violence hundreds of thousands of landless peasants/rural proletarians have occupied large tracts of unused land.

Although it is clear that food prices are so low that they are not a major factor in tying people into the capitalist system (rents, mortgages and bills do so far more effectively) it seems to us that a population capable of and actively involved in producing much of its own food outside of the money economy will be in a stronger position in the event of large scale struggles against capitalism involving strikes, lockouts, occupations and campaigns of non-payment etc. Many thousands of people are being forced by the government to take low-paid, shitty jobs or mickey mouse workfare schemes and threatened with loss of benefit if they refuse. We could support that refusal by offering surplus food from allotments and gardens to those suffering the state’s oppression. There is also the possibility of people developing similar independence from the money economy in other spheres as well — housing, energy production, waste management, health care etc which would also be highly beneficial but which is beyond the scope of this text. So to summarise our practical response should consist of: 1) a massive campaign of direct action; 2) a consumer boycott and propaganda campaign against corporate injustice, focussing on issues of sustainability and social justice; and 3) attempts at collective withdrawal from the industrialised food production system.
#anarcho-communism#anarcho-primitivism#anti-capitalism#capitalism#class#class struggle#climate crisis#colonialism#deep ecology#ecology#global warming#green#Green anarchism#imperialism#industrialization#industrial revolution#industrial society#industry#mutual aid#overpopulation#poverty#social ecology#anarchism#anarchy#anarchist society#practical anarchy#practical anarchism#resistance#autonomy#revolution
4 notes
·
View notes
Note
So I definitely agree with you that those living rurally need different, non-urban solutions. I have lived both rurally and urbanely, and I’m a big proponent of improving public transit. I think a good solution (especially because a lot of rural people work in the city) is creating park and ride spaces where people can park for the day and transit into the city.
oh this is an INCREDIBLY important part of the puzzle and one i use whenever i can when i have to go into urban centers (which to be clear isn’t super often), both to reduce congestion and because to be honest driving in the city and driving in the country are completely different skillsets. but the fact remains i think we can work on some solutions in rural areas that don’t mean giving up your cars - brianna brucespringsteendotcom mentioned their friend who worked in urban planning and because of the area found that ev charging stations were more useful for sustainability initiatives than public transport because of the type of town it was, and i think we can continue to encourage changes in behavior without throwing out the entire system.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
book review - ecotopia by ernest callenbach
Ecotopia, written by ernest callenbach in the 1970s, describes a world in which the land regions previously known as northern california, washington, and oregon secede from the rest of the united states and create their own nation, the nation of Ecotopia. the principles of sustainability and circular economy are central to this new nation.
here are my thoughts on some things covered in the book, i hope that this reaches someone else who's read it and we can share thoughts!
(this will include spoilers. however, the nature of the book is not a narrative, and is rather a presentation of ideas. therefore reading this post will not ruin the book for you if you choose to read it)
one of the greatest thought experiments Ecotopia undertakes is that of ideal urban planning. in that respect, the book is pretty cool! they hypothetical nation of Ecotopia describes San Francisco as a central city hub, from which spokes of public transport emerge and run to smaller city towns. these towns take the place of suburbs, which were razed during the country’s Independence / reconstruction era. (wooooo!!) public transport abounds and runs at a high speed of 30 mph, which is all you really need since the urban centers are so densely built and multi use. Between city towns are managed forests (actual forests! not monocultures) as well as natural land which has been allowed to restore itself.
people live in flexible communes that typically work together to produce something, whether that be a farming commune, fishing commune, artist communes, or business / science communes that invent things. everyone has a universal base income that is just minimal enough to reasonably get by, allowing people to pursue art or a risky startup without fear of dying. which i think is really cool! necessity breeds innovation yes but you need security too. work culture in Ecotopia is also vastly different, as the boundary between work and leisure and personal time is eroded, which may seem like a bad thing but the consequence of the UBI system means that most Ecotopians actually Like their work and choose to do it of their own free will. crazy huh.
houses are typically made of wood, which to me raised a suspicion flag, cause this is the Bay Area we’re talking about, which is Humid as Shit, and the Ecotopians have phased out paint due to it containing heavy metals. which good for them i guess but those houses are gonna rot lmfao. i took the liberty of imagining they are proofed with sealant made from the biodegradable, non petroleum based plastic the Ecotopians had developed and manufactured. while wood is the building material of choice, houses are also built from large tubes of insulated bioplastic, which are joined at the whim of the family or commune creating the house. (there are no architects, everyone builds their own houses themselves to suit their needs.) these houses are cheap and accessible, and zoning laws seem to be nonexistent, making homelessness a nonissue.
in terms of materials, everything in Ecotopia is renewable and has a full zero waste lifecycle. wood is the material of choice. the only metal Ecotopians use comes from scavenged cars and machinery of the pre seccession era. Ecotopians still manufacture plastic, but most kinds of it are fully biodegradable in a few days. when a lasting material is needed, a different type of plastic is used; this kind will not degrade until it is in full contact with soil. given how important disposable plastic is for applications such as research, i'm glad this was considered and accounted for in this book instead of throwing it off as a "we don't need plastic anymore kumbaya" kinda vibe.
culture wise, there is a lack of emotional restraint which the book’s narrator, a visitor from NYC, frequently comments on. hugs and physical affection between all relationships and genders are normalized. there also seems to be an insistence on small talk as a way to humanize those working “lesser skilled” jobs. honestly i found this a bit annoying, as i don’t think small talk is necessarily indicative of human connection, and that a truly emotionally attuned people would be okay with giving space when necessary. but i thought it was nice to acknowledge that all people are people, even while working “subservient” jobs.
ok so those were the things i liked.
criticism #1.
WILLIAM WESTON STOP BEING A FUCKING MISOGYNIST CHALLENGE
alternatively:
ERNEST CALLENBACH WRITE ONE (1) WOMAN WHO ISN’T A SEX OBJECT CHALLENGE
NO, THE WOMAN WHO YOU DESCRIBED AS UNATTRACTIVE WHO ALSO HAPPENS TO BE IN A POSITION OF POWER DOES NOT COUNT
god jesus christ
over the course of his adventures, journalist William Weston encounters many fellows (men) and new friends whom he talks around the fire with (men). he also encounters Marissa, a beautiful wild woman, exotic and mysterious who runs through the forest, cares deeply for trees, stares into his soul with her plain face and round dark eyes, and has sex with him twenty four hours three hundred sixty five days a year.
he also encounters Linda, an attractively sarcastic yet caring nurse, who nurses his injuries, jacks him off, and consumes him with thoughts of when he “will be healed enough to fuck her properly”. (direct quote)
in addition to the misogyny, there appears to be a fair amount of gender essentialism in Ecotopian society, something I found disappointing. Ecotopian clothes are sharply gendered. (from my understanding of Ecotopian values, i’d expect everyone to be wearing skirts due to the ease of manufacture and resulting ease of movement.) women are described to have an “air of fertility” (yes, actually). the governing party is made up of women, due to womens’ “natural competency regarding cooperation and diplomacy rather than competition”. the only sport in the country, the ritual war games, is barred to women. (it’s actually remarked later in the book that in Ecotopian psychology offices, it is often women who come in with issues of untamed aggression, and attributes it to their exclusion from the games. i wonder what a solution could be 🤔) thankfully work is not gendered, but it appears the social spheres of men and women rarely intersect, as Weston socializes and discusses ideas with a fair amount of men, and no women. perhaps for the better, as he’d be too distracted trying to fuck them to have a discussion of any substance.
queer pairings are also mentioned offhand, but they serve the purpose of emphasizing the Ecotopian's open attitudes towards sex and intimacy. queerness is treated as a sexual quirk rather than as an orientation.
in addition to the disappointing sexism / heterosexism, there's a good amount of racism. different races live segregated. although this is a conscious choice by the inhabitants, it still strikes as somewhat odd that there wouldn't be a way for humans to maintain their culture while living in an integrated society. many of the barriers to race equality in our current system are abolished in Ecotopia; the cheapness of the bioplastic houses makes it accessible for anyone to own a house anywhere, and the ease with which people can start their own enterprises reduces employment barriers significantly. therefore i'd expect integration between races to be a significant achievement of the Ecotopians. the writing itself is also racist. callenbach makes distinctions while describing the cultures of the nonwhite populations that make it clear that white is the default of Ecotopia, and all other cultures are side notes. also, callenbach makes no mention of an Ecotopian prison system (an aspect of society that no doubt merits analysis) until he mentions the Black community. sir what is up with that 🤨
there's also a lot to be said of callenbach's treatment of Indigenous ideas. the Ecotopians take a lot of inspiration from classic Indigenous principles, such as living in balance with the earth's natural resources and respecting nonhuman life, and Indigenous clothing styles. however, this feels rather appropriative rather than appreciative, and there are no actual Indigenous characters in the book. i would expect that such an empathetic society which takes direct principles from Indigenous culture would appreciate and honor the Indigenous people within that society rather than just shamelessly taking their culture, especially given the context that Ecotopians are ex citizens of the united states, the country which caused the Indigenous communities in that area so much harm.
overall, i think this book's strengths lie in its rethinking of what society could be like without work as its central focus. i love the UBI system, the reduced work week, and the attitude of work as something to enjoy rather than something to get over with. i also love that the nation's economic fall wasn't skipped over. i think its important to realize that many policies which would improve human health and quality of life would also lower our GDP, and that maybe that's perfectly fine. maybe human lives matter more than how rich a nation is. despite all these strengths, however, the sexism and racism cannot be overlooked; they made me almost put the book down several times. this book is clearly a product of its time, written by a white man. in keeping with good critical thinking practices, its important to recognize what ideas are good to keep and what needs to be thrown out.
tldr: great ideas about an alternative structure for society, unfortunately sexist and racist as well. 6/10
#gonna spam tags in hopes that it finds someone who's read it •_•#ecotopia#ecopunk#solarpunk#urban planning#utopia#sustainability#ecology#sci fi novels#sci fi#environmentalism#currently reading#books#bookblr#politics#public transportation#ernest callenbach#UBI#book review
46 notes
·
View notes
Text
The King and Queen will undertake a State Visit to France, from Wednesday 20th to Friday 22nd September 2023
The visit will celebrate the United Kingdom’s relationship with France, marking our shared histories, culture and values.
Themes and Programme Details
The State Visit will highlight the strength of the U.K.’s bilateral relationship with France, demonstrating the many ways the two countries are working together, whether that be to promote and protect biodiversity, combat climate change, strengthen security and defence ties in response to the conflict in Ukraine or recognise outstanding literary achievement.
Their Majesties’ visit will also include engagements highlighting sustainability and the power of community – key themes of importance to the citizens of both our nations.
The State Visit Programme
Their Majesties will travel to France on Wednesday 20th September and depart on Friday 22nd, undertaking engagements in Paris and Bordeaux. Highlights of their French programme will include:
In Paris:
The King and Queen will join President and Mrs. Macron for a ceremony of Remembrance and wreath laying at the Arc de Triomphe, marking the shared sacrifices of the past and an enduring legacy of cooperation.
His Majesty will have a bilateral meeting with President Macron at the Elysée Palace.
Their Majesties will be guests of honour at a State Banquet hosted at the Palace of Versailles by President and Mrs. Macron.
Their Majesties will meet community sports groups and well-known sports stars, to show the benefits sport can bring, particularly to young people, as France hosts the Rugby World Cup.
The King will address Senators and members of the National Assembly at the French Senate.
The Queen, together with Mrs. Macron, will launch a new Franco-British literary prize at the Bibliothèque Nationale de France.
His Majesty and President Macron will attend a sustainability reception for British and French business leaders, to hear more about their plans to invest to protect biodiversity and combat climate change.
In Bordeaux:
His Majesty will meet emergency workers and communities affected by the 2022 Bordeaux wildfires, at the Forêt Experimentale, a site designed to monitor the responses of urban forests to climate change.
Their Majesties will meet U.K. and French military personnel to hear more about how the two nations are collaborating on defence.
The King and Queen will attend a GREAT campaign event in Bordeaux, which will showcase British and French businesses and will provide an opportunity for Their Majesties to meet members of the French and British communities in the city.
The Royal couple will tour an organic vineyard, which has pioneered a sustainable approach to wine making.
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Philosophy of Metropolitanism
The philosophy of metropolitanism centers around the unique social, cultural, and economic dynamics of metropolitan (urban) areas and examines how these environments shape human experience, social structures, and values. Metropolitanism views cities as hubs of diversity, innovation, and complex social interactions, which stand in contrast to more traditional or rural ways of life.
Key Themes in Metropolitanism
Urban Identity and Cosmopolitanism: Metropolitanism often emphasizes cosmopolitan values, where individuals are exposed to a range of cultures, ideas, and lifestyles. Cities foster a sense of open-mindedness and adaptability, as people encounter diversity and interact with individuals from various backgrounds.
Collective and Individual Identity: In metropolitan environments, there is often a tension between collective urban identity (e.g., being a New Yorker, Londoner) and the individual’s quest for uniqueness. City life often supports personal expression while also creating a shared cultural experience within neighborhoods, workplaces, or social circles.
Innovation and Progress: Cities are frequently seen as engines of progress and change. The metropolitan lifestyle values innovation and entrepreneurship, spurred by dense social and economic networks that encourage rapid exchange of ideas, resources, and opportunities.
Alienation and Anonymity: Metropolitanism also considers the challenges of urban life, such as alienation, stress, and a sense of disconnection, despite being surrounded by people. Some argue that cities can lead to impersonal relationships, as individuals are constantly moving and adapting to the fast pace of urban life.
Social Complexity and Hierarchies: Cities create complex social structures, with different socioeconomic classes, professional networks, and communities. Metropolitanism examines how these layers contribute to both opportunity and inequality, and how urban policies impact issues like gentrification, housing, and public services.
Public Space and Community: The philosophy of metropolitanism also considers the importance of public spaces—parks, squares, and cultural sites—in fostering social cohesion and community life. These spaces serve as places for connection, recreation, and political expression, balancing the private and public spheres in dense urban landscapes.
Environmental and Sustainability Concerns: Urban environments are increasingly under scrutiny for their impact on the natural environment, and metropolitanism encompasses discussions on sustainable city planning, green spaces, and the need for eco-friendly solutions to address issues like pollution, traffic, and energy use.
Philosophical Perspectives on Metropolitanism
Urbanism and the Human Condition: Thinkers like Georg Simmel and Walter Benjamin have explored how city life affects the individual’s psyche, noting that the sensory overload and rapid pace of cities influence people’s ways of thinking and relating to one another.
Metropolitanism and Social Theory: Urban theorists, such as Henri Lefebvre, emphasize the “right to the city,” which argues that city residents should have a say in urban planning and access to its resources, promoting an ethical perspective on urban living.
Globalization and Cultural Exchange: Cities are often at the forefront of globalization, and metropolitanism reflects this interconnectedness, where metropolitan areas serve as cultural and economic nodes in a global network. This raises questions about cultural preservation, assimilation, and the impacts of international influence on local customs.
Critiques of Urban Capitalism: Many theorists critique the capitalist structures prevalent in urban centers, arguing that metropolitan areas often become sites of economic disparity, where wealth and poverty are starkly juxtaposed. Scholars like David Harvey analyze how urbanization serves capitalistic interests, often prioritizing profit over the welfare of city dwellers.
Postmodern Urbanism: Postmodernist thinkers suggest that metropolitan life challenges traditional norms and hierarchies, giving rise to new forms of community, identity, and cultural expression. The postmodern city is seen as a space of fragmentation but also of new opportunities for redefining social relations.
Influence and Application of Metropolitanism
Metropolitanism has practical implications in urban planning, sociology, and environmental policy. It influences how cities are designed, addressing issues of accessibility, inclusivity, and sustainability. Additionally, metropolitanism shapes cultural policy and education, as cities are hubs for art, music, and intellectual exchange. It also informs political theory, with cities often being centers for social movements and advocacy for issues like civil rights, environmentalism, and economic equality.
#philosophy#epistemology#knowledge#learning#education#chatgpt#Metropolitanism#Urban Philosophy#Cosmopolitanism#Urban Identity#City Life and Community#Social Theory and Urban Studies
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo

The Williamsburg Bridge continues to serve as a symbol of progress, connectivity, and resilience in the heart of New York City. Its enduring presence and multifaceted importance make it a cherished and celebrated landmark in the city's history and culture.
Commemorative Events: Periodically, the Williamsburg Bridge is the focal point for events commemorating significant milestones, historical anniversaries, or community celebrations. These events bring together residents, visitors, and local organizations to celebrate the bridge's significance.
Sustainability Initiatives: In alignment with broader sustainability efforts in New York City, there has been a growing emphasis on making the Williamsburg Bridge more environmentally friendly. This includes exploring ways to reduce energy consumption for lighting and implementing eco-friendly practices in maintenance and construction.
Connecting Communities: The bridge serves as more than just a physical connection; it also connects the people and communities on either side of the East River. It has played a role in shaping the identities and cultural exchanges between Manhattan's Lower East Side and Brooklyn's Williamsburg neighborhood.
Educational Tours: Educational tours and programs often feature the Williamsburg Bridge as a case study in civil engineering and architectural history. Students and enthusiasts can learn about its construction, design, and ongoing maintenance.
Transportation Innovation: As transportation technology evolves, discussions have arisen about how the Williamsburg Bridge can adapt to accommodate new forms of mobility, such as electric scooters and shared transportation services, to meet the changing needs of city residents.
Civic Engagement: The bridge has been a platform for civic engagement and public demonstrations. Throughout its history, it has been the site of protests, marches, and gatherings where people come together to advocate for various causes and express their views.
Architectural Photography: The bridge's striking architectural features, including its towers, suspension cables, and intricate details, have made it a subject of interest for architectural photographers and enthusiasts.
Resilience Planning: In the face of climate change and extreme weather events, city planners are increasingly focused on ensuring the resilience of critical infrastructure like the Williamsburg Bridge. Measures are being explored to fortify it against rising sea levels and potential storm surges.
Continued Innovation: Engineers and architects continue to explore innovative methods and materials to extend the lifespan of the Williamsburg Bridge and ensure its safety for generations to come.
Artistic Inspiration: Beyond being a subject for photographers, the Williamsburg Bridge has also inspired artists and writers. It has appeared in literature, paintings, and other creative works, often serving as a symbol of urban life and aspiration.
Historical Preservation Efforts: Preservationists and historians have worked diligently to ensure the bridge's historical integrity is maintained. This includes efforts to protect and restore the bridge's architectural features, which are essential for its designation as a historic landmark.
Economic Benefits: The Williamsburg Bridge has played a significant role in facilitating commerce and trade between Brooklyn and Manhattan. It has supported businesses, industries, and economic growth in both boroughs, contributing to the overall prosperity of the city.
Educational Resources: The bridge serves as an educational resource for schools, universities, and institutions interested in studying urban infrastructure, transportation systems, and architectural history. It offers valuable insights into engineering and design principles.
Public Art Installations: Occasionally, the bridge has hosted public art installations that interact with its architecture and surroundings. These installations often engage the public in unique ways and spark discussions about art and urban spaces.
Ceremonial and Parades: The Williamsburg Bridge has been a route for various parades, processions, and ceremonial events, including the annual New York City Marathon, which crosses the bridge as part of its course.
Bridging Communities: The bridge has been a symbol of unity and connection between Manhattan and Brooklyn, fostering cultural exchanges and collaborations between the two boroughs.
Film and Television: The Williamsburg Bridge has appeared in numerous films and television shows, contributing to its recognition worldwide. It has been featured in a range of genres, from dramas to action movies.
International Recognition: The Williamsburg Bridge's iconic design and historical significance have led to its recognition on the international stage, with tourists from around the world coming to see and photograph the bridge.
Transportation Network Integration: As part of New York City's extensive transportation network, the Williamsburg Bridge connects to a vast network of roads, highways, subways, and buses, enabling easy access to various parts of the city and the metropolitan area.
The Williamsburg Bridge remains a cherished icon of New York City, symbolizing its history, diversity, and unwavering spirit. Its enduring presence and cultural significance continue to shape the city's landscape and the lives of those who call it home.
<Previous page - Williamsburg Bridge - Next page>
#New York City#new york#newyork#New-York#nyc#NY#manhattan#urban#city#USA#buildings#visit-new-york.tumblr.com#bridge#Williamsburg Bridge
138 notes
·
View notes
Note
I'm a big fan of building commie blocks to ameliorate the US housing crisis -- and putting them in the public parks that were stolen from other communities to give colonisers some trees to look at -- but what policies should be enacted to get suburbanites into beautiful and efficient bedspace apartments with kitchens and washrooms shared by a floor?
As a good social democrat, I'm contractually obligated to prefer Red Vienna to your proper commie block. Short of a complete class revolution that completely upends the social hierarchy, a significant part of ensuring that social housing pulls off being "a living tapestry of a mixed community" is building it to middle-class standards (including aesthetic standards) so that people with the money to find alternatives don't all leave. Art Deco is a hell of a lot chic-er than the boring minimalist crap that luxury developers are getting away with these days.

Also, don't build them in parks: green space is not only important for environmental sustainability but also the health and mental health of working-class and poor communities who can't afford houses in the suburbs, and we should be encouraging in-fill development instead. (Build them on golf courses instead, because they are classist, invasive, artificial monocultures that do nothing for the environment.)
In terms of how to make suburbia more in synch with dense, sustainable social housing, there are a number of necessary changes:

Commuter rail: suburbs predate the car by a fair few decades, and originally sprung up along the routes of commuter rail lines. Well, it turns out that transit-oriented development and dense transit corridors go hand-in-hand: if you can build higher-density units near transit lines, people will use mass transit to commute, and if there are well-planned areas of higher density around major urban areas, the increased number of commuters can support more regular transit services.
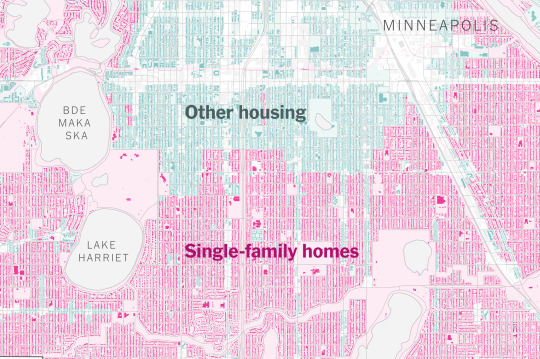
Planning/zoning/ligitation revolution: as I mentioned in my student housing post, one of the major reasons why it's so hard to build affordable housing projects is that local NIMBY groups use every legal tool in the book to bury them. So there needs to be pretty comprehensive reforms of zoning regulations (banning single-family zoning, reducing set-backs and eliminating mandatory parking, getting rid of "unrelated persons" limitations, getting rid of building heights limits, etc.), standardization of the permitting and development approval process, streamlining of the public comment/hearing process and environmental review process for model projects, and extreme limits on litigation for model projects.

Financing reform: as I sort of imply in my Red Vienna section above, a big part of making social housing/public housing successful and avoiding replicating or increasing class and racial segregation is adhering to middle-class minimum standards. This has important knock-on implications:
you need to eliminate requirements for absolute lowest possible land costs (which restrict social housing to economically and socially isolated areas).
you need to raise allowable construction costs, so that you can achieve those aesthetic standards and avoid corner-cutting like smaller rooms and lower ceilings, single-thickness walls/floors/ceilings, no doors on cabinets or closets, cheap cladding and wiring and pipes and other building materials, low-quality insulation and HVAC, etc. Not only do middle-class folks notice this stuff and go elsewhere, but it's all penny-wise and pound-foolish, because cheap construction runs down faster which increases maintenance costs, and sometimes it just straight-up kills people.
you need to adequately finance maintenance, services, and amenities. This is crucial to keeping tenants with deeper pockets, but it's also another one of those things where penny-pinching is counter-productive in the long-run. The more you save on maintenance costs, the faster the buildings run down and the more expensive repairs you have to make. The more you save on services like superintendants and doormen, the more your tenants end up having to spend on handymen and the more you have to spend on police and repair costs. And so forth.
And there is a real potential here for all kinds of positive feedback loops: spending money on achieving higher standards of construction and operation means that you can hang onto and attract higher-income tenants, which means you can have sliding scale rents that cross-subsidize tenants and pay for higher construction and operating costs, and the poor and working class tenants who couldn't have paid for those higher costs and amenities on their own enjoy a "positive externality" for once.
#public policy#public housing#social housing#social democracy#urban development#urbanism#urban planning#urban studies#housing#nimbyism#nimby#red vienna#commie blocks
112 notes
·
View notes
Text
Rajvardhan Rathore Welcomes the Saudi Arabia Delegation at Rising Rajasthan 2024
Rajasthan, often known for its rich culture, history, and vibrant tourism, recently took another bold step in expanding its global footprint with the grand event of Rising Rajasthan 2024. The annual gathering, which showcases the state’s economic, cultural, and technological prowess, saw an exciting and significant moment when Dr. Rajvardhan Rathore, the State Minister for Sports and Youth Affairs, extended a warm welcome to the high-level delegation from Saudi Arabia.
Held in the heart of Jaipur, Rising Rajasthan 2024 aims to bring together international investors, policymakers, and thought leaders to explore new opportunities and build long-term partnerships across various sectors. The presence of the Saudi delegation underscored the growing importance of international collaboration, especially with the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, one of the largest and most influential economies in the Middle East.
A Moment of Diplomacy and Opportunity
Dr. Rajvardhan Rathore, a former Olympic medalist and a prominent leader in the Indian political landscape, played a key role in facilitating this important diplomatic encounter. As an advocate for both sports and sustainable development, his leadership at Rising Rajasthan 2024 was instrumental in setting the stage for deeper ties between Rajasthan and Saudi Arabia.
In his opening remarks, Dr. Rathore emphasized the strategic potential of Rajasthan in various sectors, from renewable energy and infrastructure to tourism and education. He highlighted the state’s rich cultural heritage and diverse opportunities for collaboration, inviting Saudi businesses and entrepreneurs to explore the many avenues for investment in Rajasthan.
“Rajasthan is not just a state; it’s an embodiment of India’s diversity and strength. We believe that our growing relationship with Saudi Arabia, particularly in areas of commerce, energy, and culture, will lead to a future of shared prosperity and innovation,” Dr. Rathore said, addressing the delegation.
The Saudi Delegation’s Vision for Rajasthan
The Saudi delegation, led by prominent government officials and business leaders, expressed keen interest in exploring the abundant opportunities that Rajasthan has to offer. With Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 in full swing, the Kingdom is increasingly looking to diversify its economy and invest in new sectors, such as tourism, renewable energy, and technology.
During their visit, the Saudi representatives engaged in discussions on potential collaborations in several key areas, including:
Renewable Energy: Saudi Arabia has made significant strides in solar and wind energy, and there is tremendous potential for collaboration in Rajasthan, which boasts vast open lands and abundant sunlight. Both sides discussed possible partnerships in the energy sector, particularly in large-scale solar power projects.
Tourism & Hospitality: Rajasthan, with its rich history, forts, and palaces, is already a major tourist destination. The Saudi delegation explored opportunities to strengthen ties between the tourism industries of both regions. This included promoting cultural exchanges, joint tourism ventures, and building better connectivity between the two regions.
Infrastructure & Smart Cities: As part of its Vision 2030, Saudi Arabia is focused on developing smart cities and modern infrastructure. Rajasthan’s government has ambitious plans for urban renewal, and the Saudi delegation showed interest in collaborating on these projects, offering expertise in sustainable urban development.
Cultural Collaboration: With deep cultural roots in both India and Saudi Arabia, there is a natural synergy between the two. The event saw discussions on fostering cultural exchanges, promoting art, music, and heritage, and building people-to-people connections.
Rajasthan’s Role in a Globalized Economy
Dr. Rajvardhan Rathore’s warm welcome to the Saudi delegation comes at a time when India, and particularly Rajasthan, is poised to play a larger role on the global economic stage. The state, with its large population, strong industrial base, and growing infrastructure, offers a wealth of opportunities for foreign investment.
In his speech, Dr. Rathore also highlighted the role of the state in India’s vision of becoming a $5 trillion economy by 2025. He stressed that Rajasthan’s growing industries, such as textiles, handicrafts, mining, and food processing, align perfectly with Saudi Arabia’s ambitions to diversify its economy.
Moreover, Rising Rajasthan 2024 provided a platform for fostering relationships beyond traditional trade. The event opened doors to educational exchange programs, collaborative research in technology, and the possibility of joint ventures in areas like artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and fintech.
The Future of India-Saudi Arabia Relations
The significance of the Saudi delegation’s visit cannot be understated. As global partnerships become increasingly important for long-term economic stability, this exchange between Rajasthan and Saudi Arabia is a step towards deeper bilateral relations.
With both nations working toward diversifying their economies and embracing technological innovation, the collaboration between them is expected to flourish in the years ahead. Rajasthan, with its strategic location, skilled workforce, and government-friendly policies, offers the perfect environment for Saudi investments.
The visit also marked a new chapter in India-Saudi Arabia relations, building on the shared cultural ties and economic interests between the two nations. By fostering dialogue and collaboration, Rising Rajasthan 2024 reinforced its role as a key platform for international partnership and a driving force for Rajasthan’s bright future.
As the curtains fell on Rising Rajasthan 2024, the collaboration between Dr. Rajvardhan Rathore and the Saudi delegation symbolized a momentous occasion for the state and its place in the global economy. The potential for growth and mutual benefit is vast, and both Rajasthan and Saudi Arabia seem poised to embark on a journey of shared prosperity and innovation.
The event was a testament to Rajasthan’s emerging position as a key player in the international arena, and with leaders like Dr. Rajvardhan Rathore at the helm, the future looks incredibly promising for the state’s growth and its relationships with countries around the world.
2 notes
·
View notes